Unveiling the Stone Age: A Journey Through the Ingenious Artifacts of Early Human Civilization
The Stone Age, a time of profound human innovation and adaptation, marked the first chapters of our collective history. It is an era defined by the ingenious artifacts that have survived the ravages of time, revealing the remarkable skills of our ancient ancestors.
In this article, we embark on a captivating journey through the annals of prehistoric times, as we unveil the best artifacts from the Stone Age. From the rudimentary but effective tools of the Lower Paleolithic to the intricate art and craft of the Neolithic period, these artifacts offer a fascinating insight into the ingenuity, culture and evolution of early human civilizations.
1. hand axes
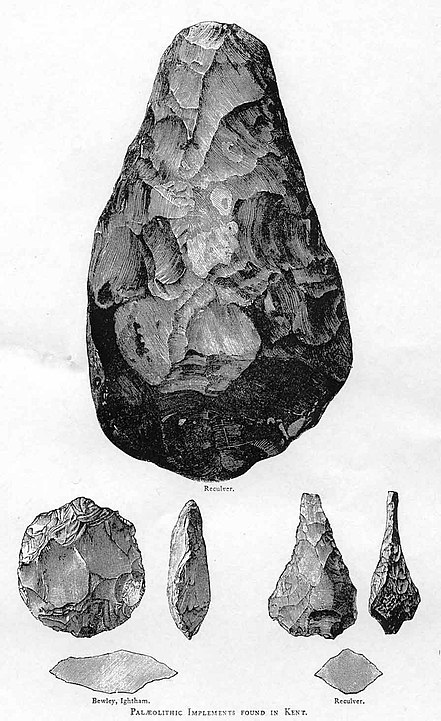

Age: Lower Paleolithic, dating back to about 1.7 million years ago.
Hand axes are iconic Stone Age tools known for their teardrop or almond shape. Made with a symmetrical design, they served as multipurpose tools for early humans, used for cutting, chopping, and even as weapons. Their existence over a wide geographic range suggests the transmission of knowledge and skills within ancient human communities.
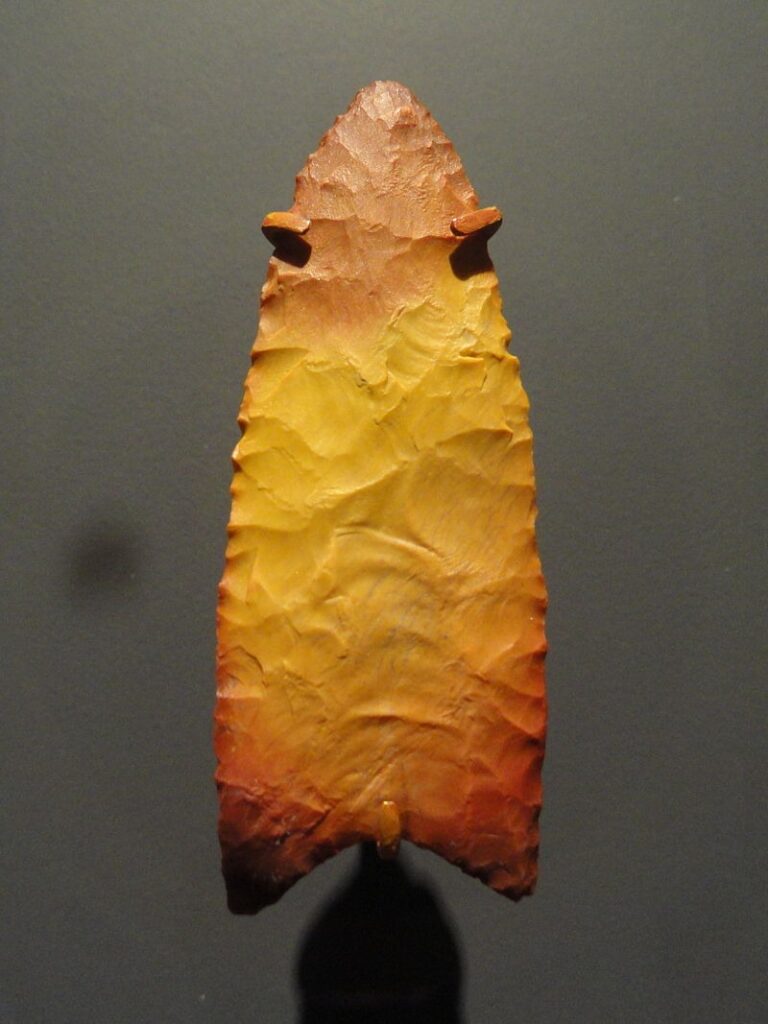

Age: Associated with the Clovis culture during the Paleoindian period, about 13,000 years ago.
Clovis tools, particularly Clovis points, are among the most famous artifacts of early North American indigenous cultures. These finely crafted stone tools were used to hunt megafauna such as mammoths and mastodons. Its elegant design, with a flute running down the center of the tip, showcases the exceptional craftsmanship of early Native American cultures.
3. Cave paintings
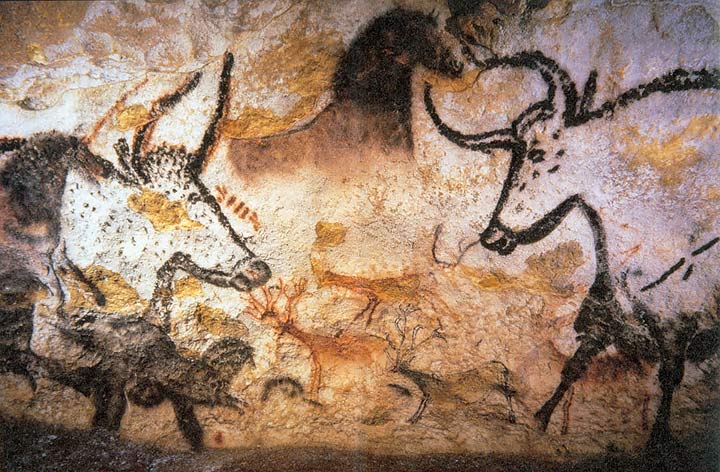

Lascaux Painting
Age: Paleolithic Period, spanning from about 40,000 to 14,000 years ago.
Some of the most captivating artifacts from the Stone Age are the intricate cave paintings found in places like Lascaux in France and Altamira in Spain. These ancient works of art offer a window into the lives and beliefs of our prehistoric ancestors. Painted on the walls of the cave, they depict animals, hunters and rituals, and their vividness and detail continue to surprise researchers and art enthusiasts alike.
4. Figures of Venus
Age: Predominantly from the Upper Paleolithic, between 30,000 and 10,000 years ago.
Venus figures are small, often voluptuous female figures carved from various materials, such as stone, ivory and clay. These figures are believed to represent fertility and possibly had spiritual or religious significance. Its prevalence in Europe and Asia suggests common cultural themes during this period.
5. Atlatl Spear Throwers
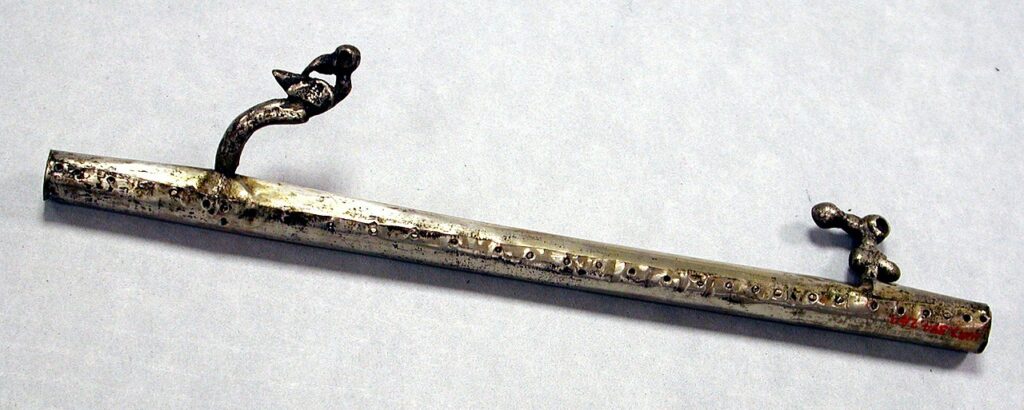 A Peruvian silver atlatl from the 12th to 15th century.
A Peruvian silver atlatl from the 12th to 15th century. 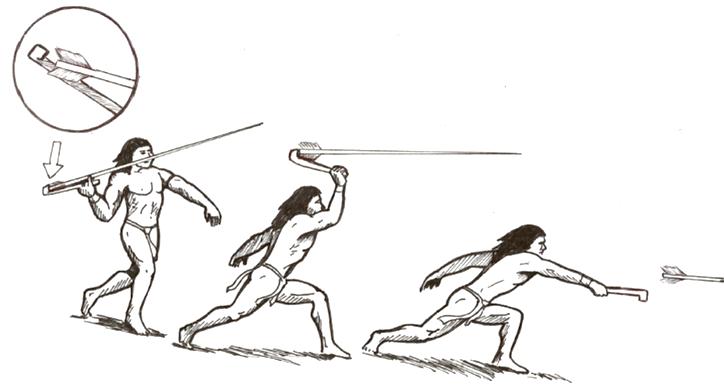
An Atlatl in use | CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
Age: Used in various periods of the Stone Age.
Atlatl spear throwers are an ingenious tool used to increase the range and force of a thrown spear or dart. They consist of a handle with a hook that grips the back of the spear, effectively lengthening the thrower’s arm. This innovation allowed our ancestors to hunt and defend themselves more effectively, marking a significant development in weaponry and hunting technology.
6. Stone adzes
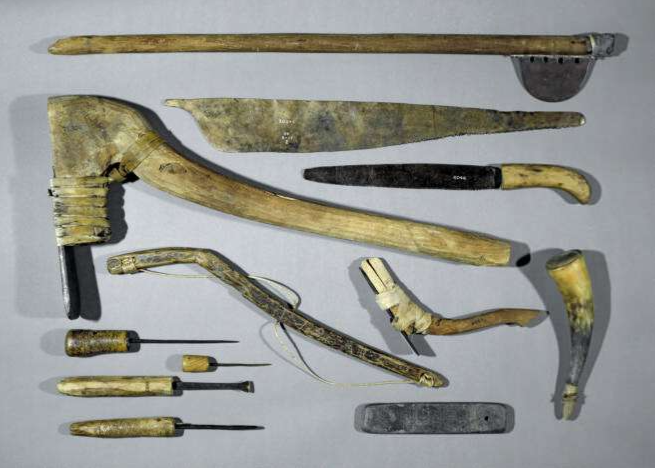

Photo source: British Museum.
Age: Used throughout the Stone Age, with variations over time.
Stone adzes were versatile tools used to cut and shape wood, making them essential for crafting shelters, boats, and other wooden objects. These artifacts demonstrate the ingenuity of Stone Age people in adapting natural materials to their needs.
7. Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc rock art
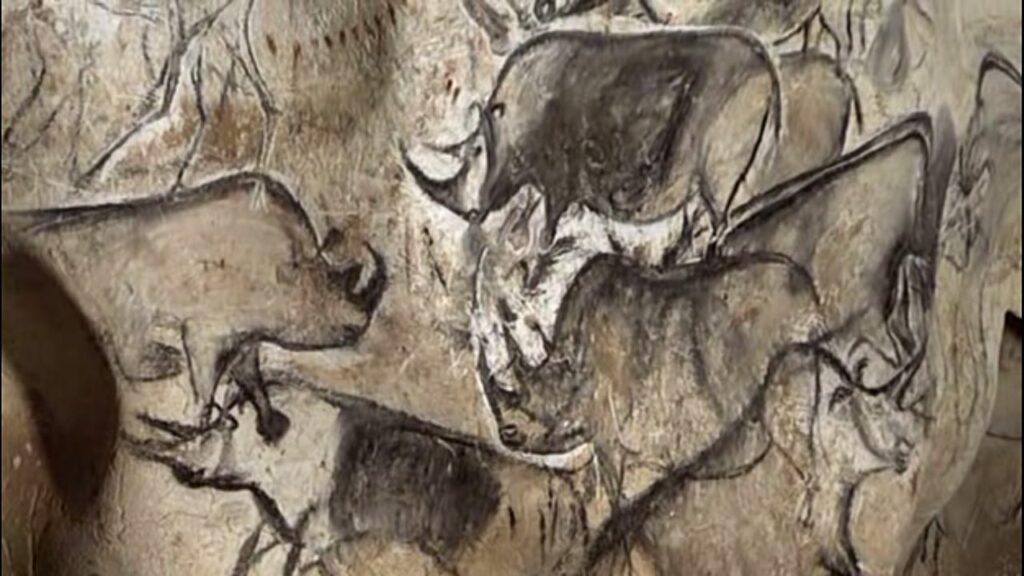 Drawings of rhinos from Chauvet Cave
Drawings of rhinos from Chauvet Cave
Age: Predominantly Paleolithic, approximately 36,000 years ago.
The Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc cave in France is famous for its impressive prehistoric works of art. The walls of the cave are adorned with intricate depictions of animals, including mammoths, lions and rhinos. The exquisite detail and quality of this art offers a rare glimpse into the artistic prowess of our ancient ancestors.
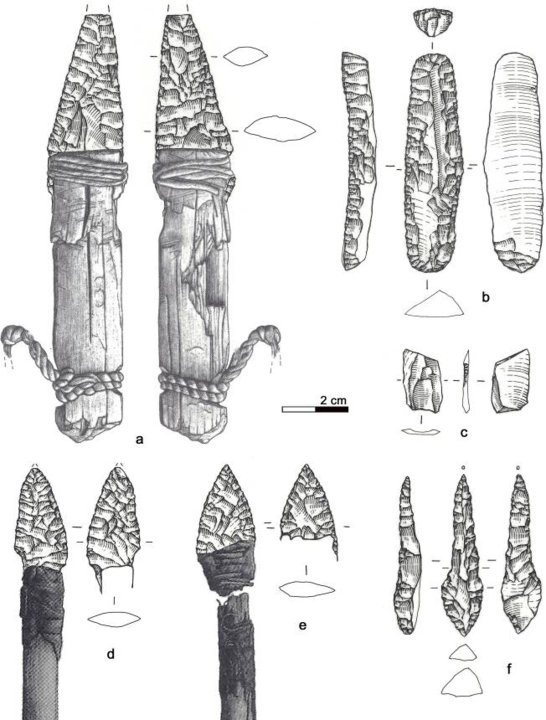
Ötzi the Iceman: Lithic assemblage a) dagger, b) scraper, c) small flake, d) arrowhead 14, e) arrowhead 12, f) borer The original title in Wierer et al read “The lithic assemblage of Iceman. a) Dagger, b) Scraper, c) Borer, d) Arrowhead 14, e) Arrowhead 12, f) Small scale. | CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
Age: Dating back to approximately 3300 BC. C. (Copper Age/Neolithic).
Ötzi, the well-preserved mummy discovered in the Alps, offers a unique window into the life of an ancient individual. Along with Ötzi, his tools and clothing were remarkably preserved, providing insights into his daily life. These artifacts include a copper axe, clothing made of various materials, and a quiver of arrows, shedding light on the technology and skills of the Neolithic period.
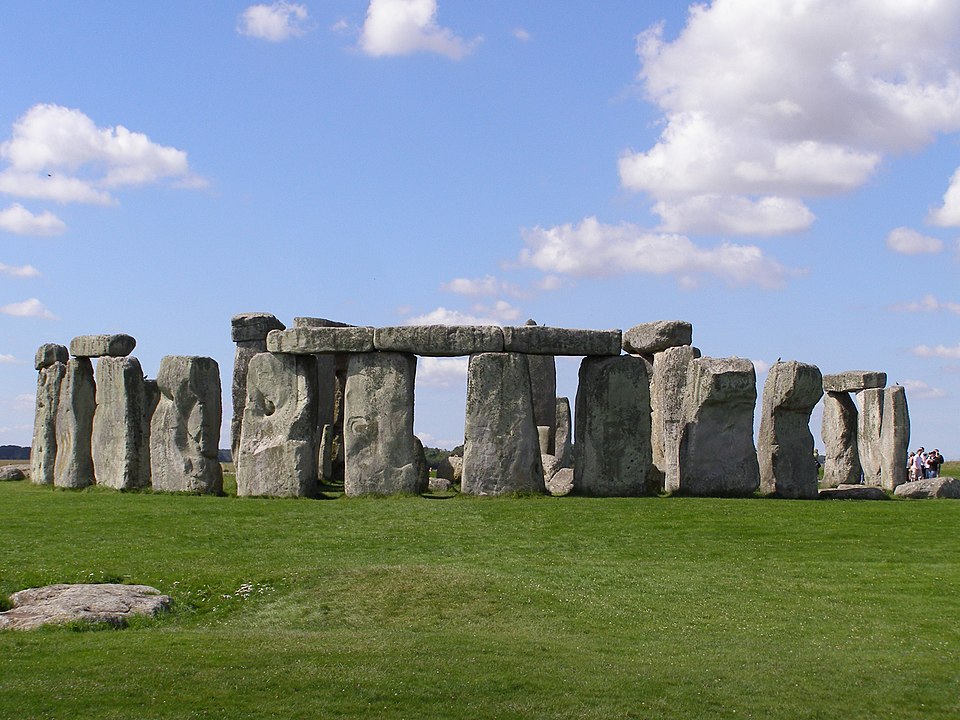
9. Stone henges
 CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
Age: Built mainly during the Neolithic period, around 2500 to 2000 BC. c.
Stone Henge, one of the most famous megalithic monuments in the world, is located in England. These henges, which comprise huge stone monoliths arranged in circular patterns, are believed to have had religious or astronomical significance. The construction of such colossal stone monuments without modern machinery remains a testament to the engineering prowess of Stone Age communities.
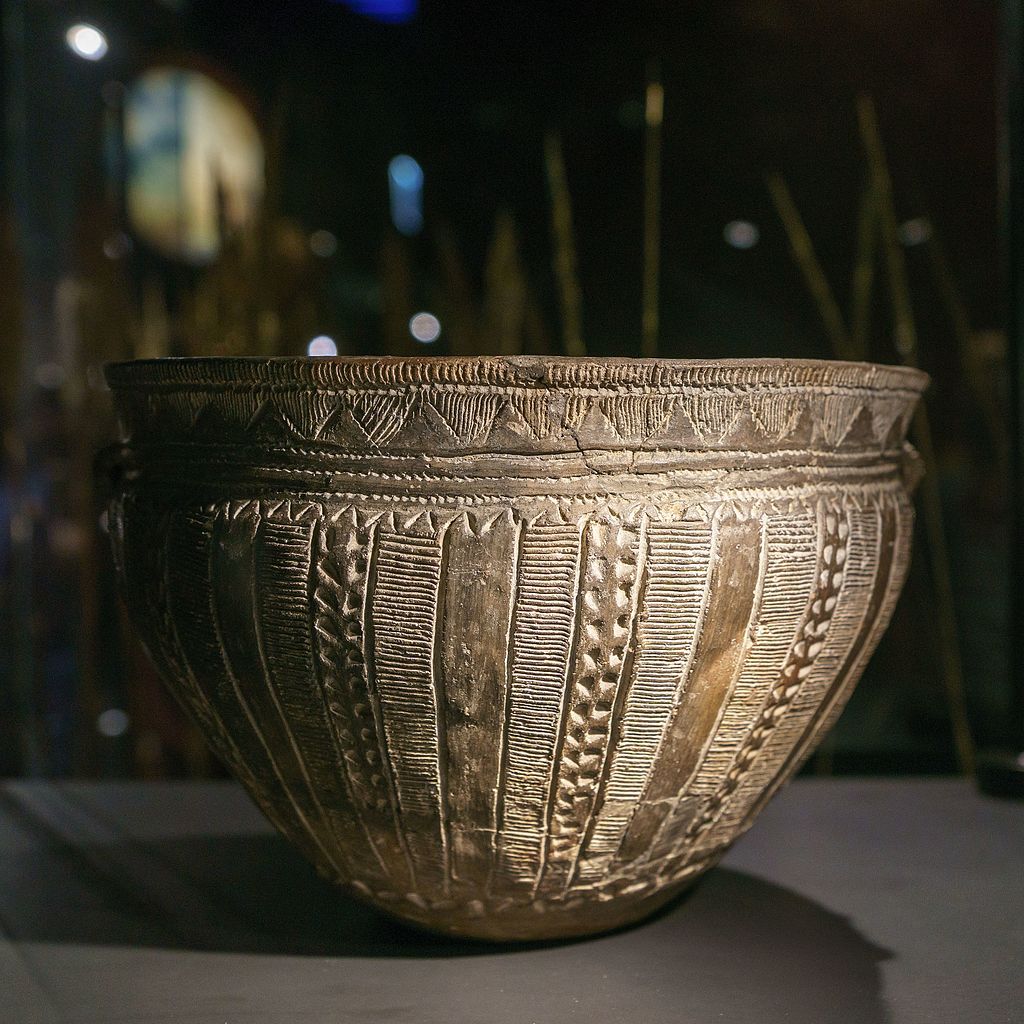
10. Stone Age Pottery
 CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
Age: Pottery production evolved over time, beginning in the Neolithic.
The arrival of ceramics marked a significant advance in the history of human technology. Early Stone Age pottery served a variety of purposes, from cooking and storage to ritual and trade. The pottery trade played a crucial role in the development of settled communities.
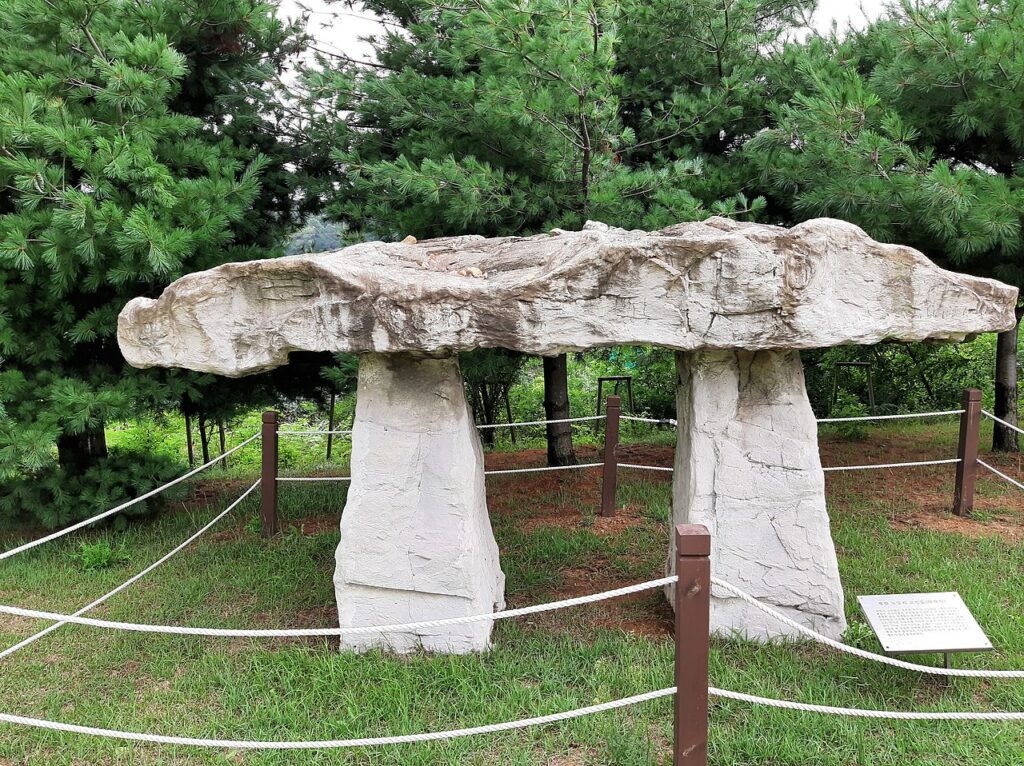
11. Dolmens
 CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
Age: Predominantly from the Neolithic period, but found in various cultures and time periods.
Dolmens are ancient megalithic structures consisting of large stone slabs, often used as burial chambers or as religious sites. These impressive stone constructions, found in various parts of the world, reflect the importance of community and spiritual practices during the Stone Age.
12. The lion man
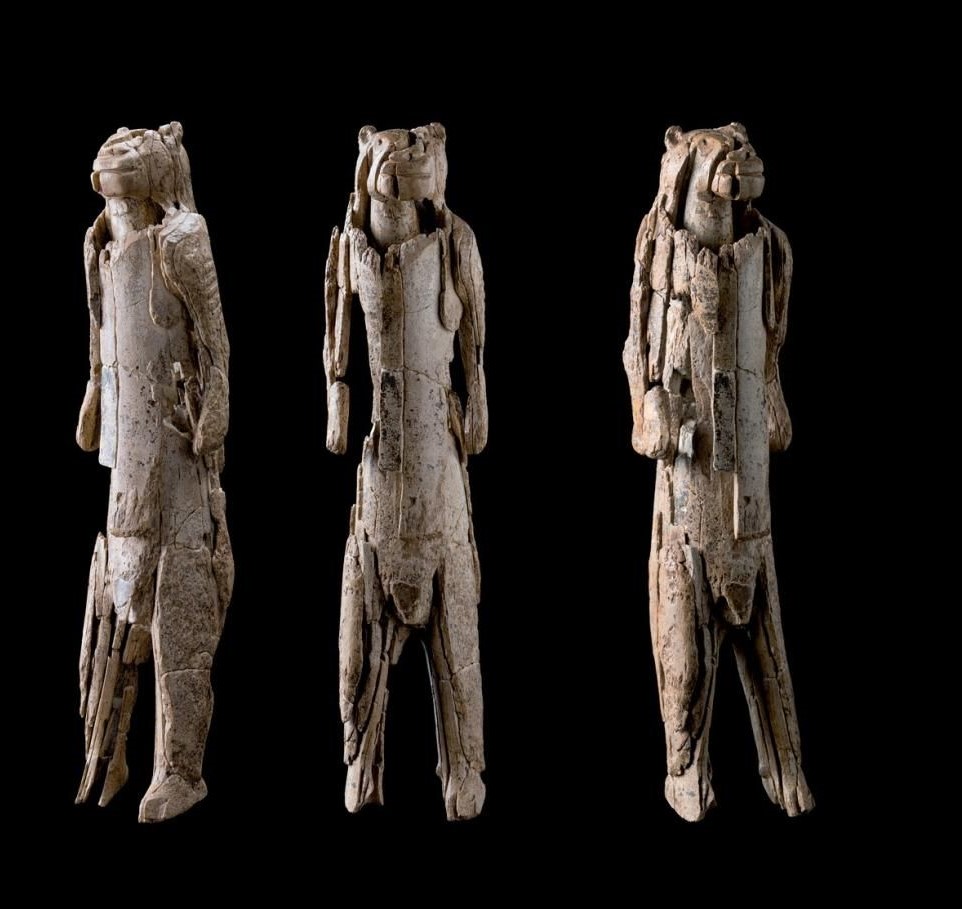 Photo source: British Museum.
Photo source: British Museum.
Age: Created during the Upper Paleolithic, approximately 40,000 years ago.
The Lion Man, or Löwenmensch, is an extraordinary artifact made from mammoth ivory. This intricately carved figure represents a humanoid with the head of a lion or big cat. It is one of the earliest known examples of figurative art and shows the artistic abilities of Stone Age people, as well as possibly hinting at their spiritual or mythological beliefs.
13. Star Carr Headdresses
Age: From the Mesolithic period, approximately 9,000 years ago.
Star Carr, a Mesolithic archaeological site in the United Kingdom, produced some unique artifacts, including headdresses made from deer skulls. These headdresses are believed to have been used in rituals, demonstrating the importance of ceremonial practices in Stone Age cultures.
14. Skara Brae
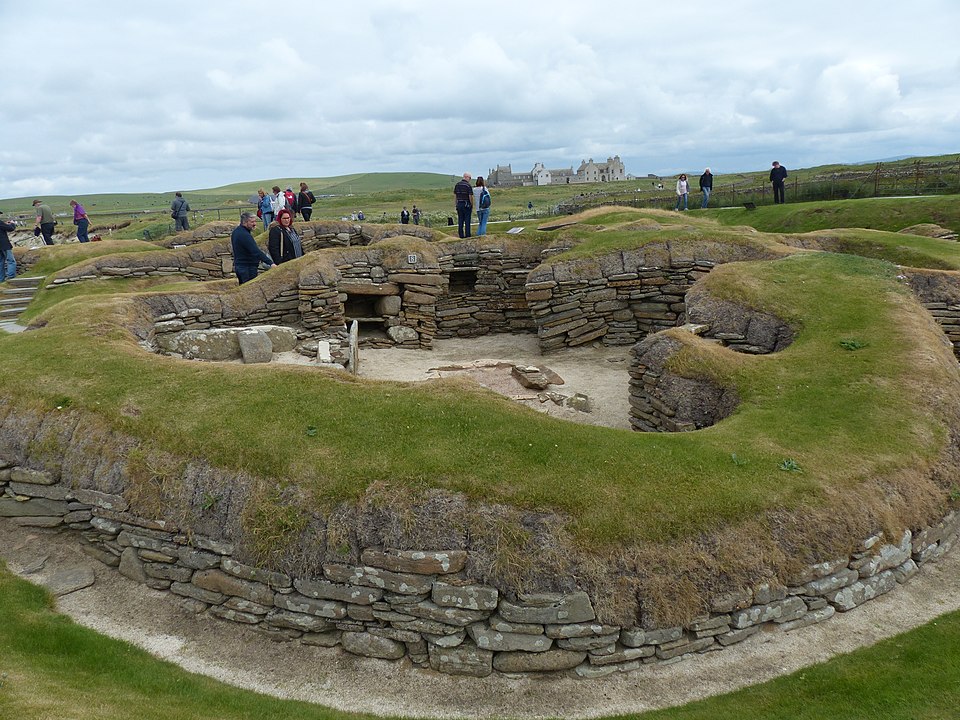 CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
Age: Neolithic, around 3200 BC
Skara Brae is a remarkably well-preserved Neolithic village on Scotland’s Orkney Islands. The stone structures of this settlement provide information about how people lived during this era, with houses, furniture and tools built from stone. The design of Skara Brae is a testament to early urban planning and community life.
15. Stone Age Jewelry
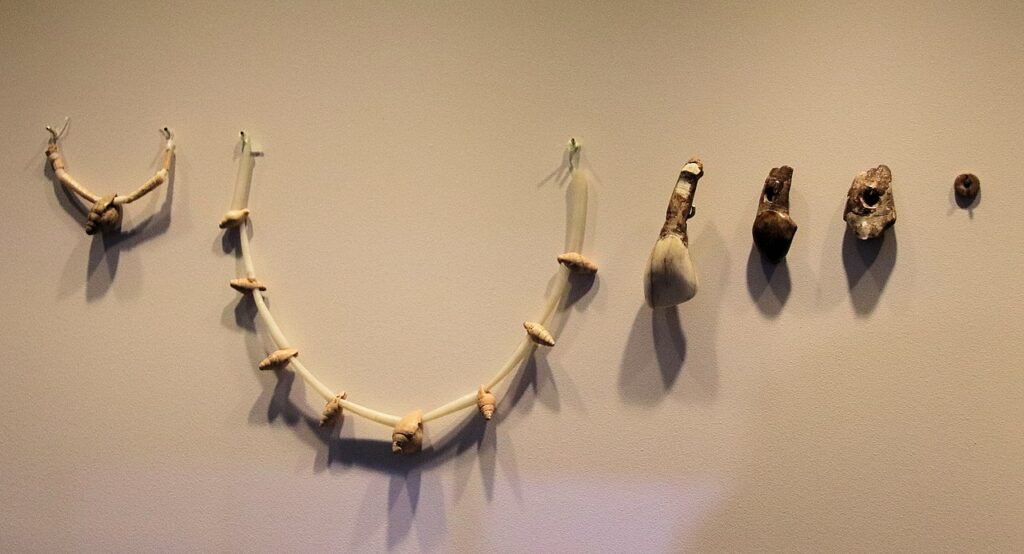 CC0 1.0 WRITING
CC0 1.0 WRITING
Age: Created and used throughout the Stone Age.
Stone Age jewelry includes beads, pendants, and other ornaments made from materials such as bone, shell, and stone. These items served not only as personal ornamentation but also as symbols of status, commerce, and possibly spiritual significance. They provide insight into the aesthetic and symbolic values of ancient cultures.
16. Stone Age Canoes
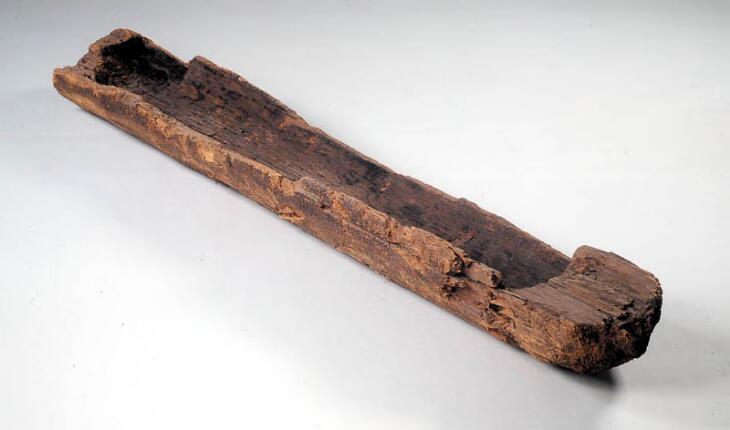 The Pesse canoe is believed to be the oldest known boat in the world. It is made from a piece of Scots pine trunk (Pinus silvestris). With the help of fire, this piece of trunk has been hollowed out, except for the front and rear ends. In many places inside this hollowed trunk there is still a thin layer of charred wood. The exterior also shows clear traces of fire. | CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
The Pesse canoe is believed to be the oldest known boat in the world. It is made from a piece of Scots pine trunk (Pinus silvestris). With the help of fire, this piece of trunk has been hollowed out, except for the front and rear ends. In many places inside this hollowed trunk there is still a thin layer of charred wood. The exterior also shows clear traces of fire. | CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
Age: Developed during various periods of the Stone Age.
Stone Age canoes were primitive boats built from hollowed-out logs. These early ships played a vital role in fishing, transportation and exploration. Its development represents a leap forward in human mobility and the use of resources.
17. Mounds

Tomb of King Alyattes at Bin Tepe in Lydia, modern Turkey, built around 560 BC | CC0 1.0 WRITING
Age: Mainly associated with the Neolithic and Bronze Age, spanning several millennia.
Burrows, also known as barrows or barrows, are artificial hills built to house the remains of the deceased. These monuments were created during various periods of prehistory and are found in different parts of the world. The mounds offer information about the funerary practices and social structures of ancient societies.
18. Alta Rock Art
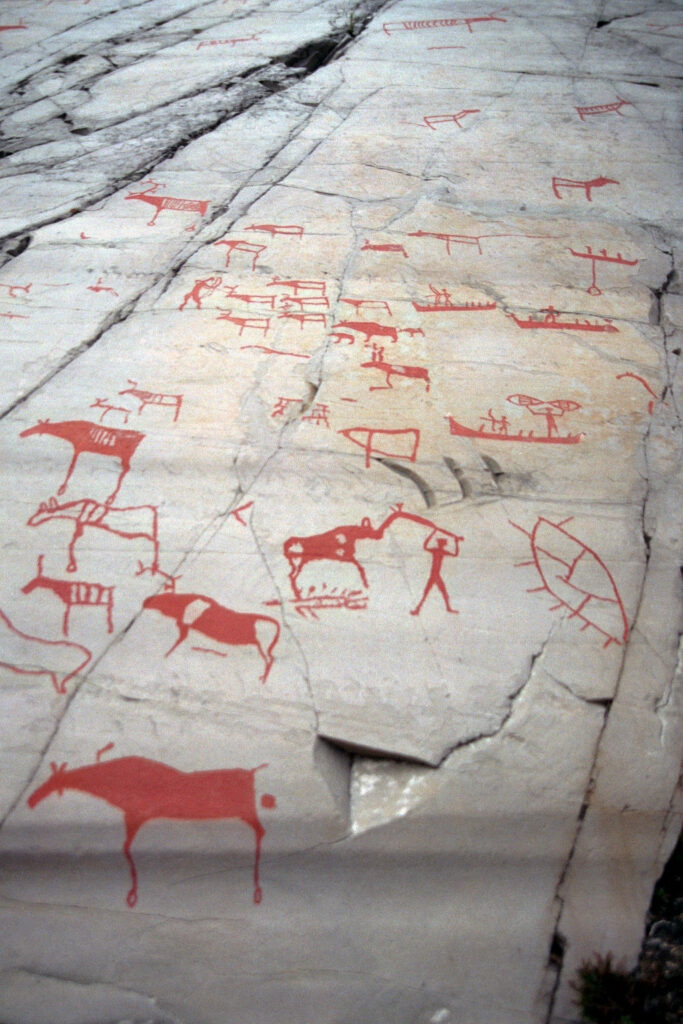

CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
Age: Predominantly Neolithic and Bronze Age, dating back thousands of years.
Alta rock art, located in Norway, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, famous for its petroglyphs, which are carvings and paintings on rock surfaces. These depictions of animals, scenes and symbols provide valuable glimpses into the spiritual beliefs and daily lives of the region’s ancient inhabitants.
19. Mehrgarh Pottery
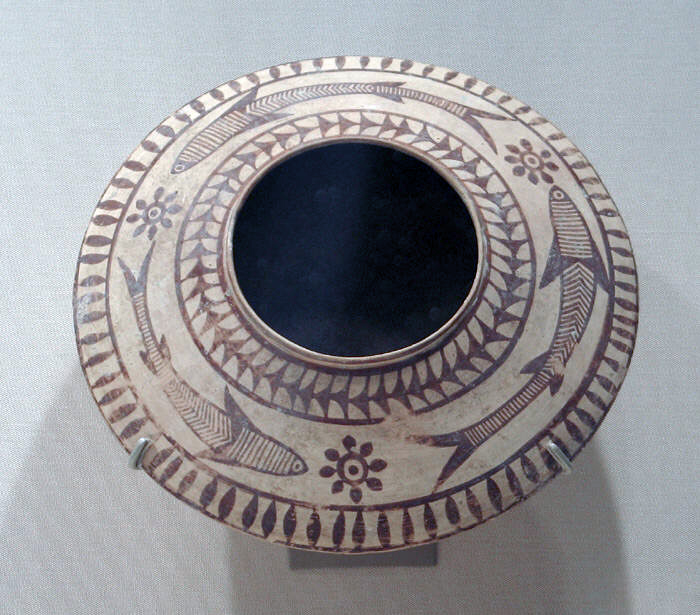

CC0 1.0 WRITING
Age: Neolithic, around 7,000 BC
Mehrgarh, in modern-day Pakistan, is an archaeological site where some of the earliest examples of pottery were discovered. These vessels and containers represent a significant step in the development of ceramic technology and indicate the shift from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to sedentary agriculture.
20. Tărtăria Tablets
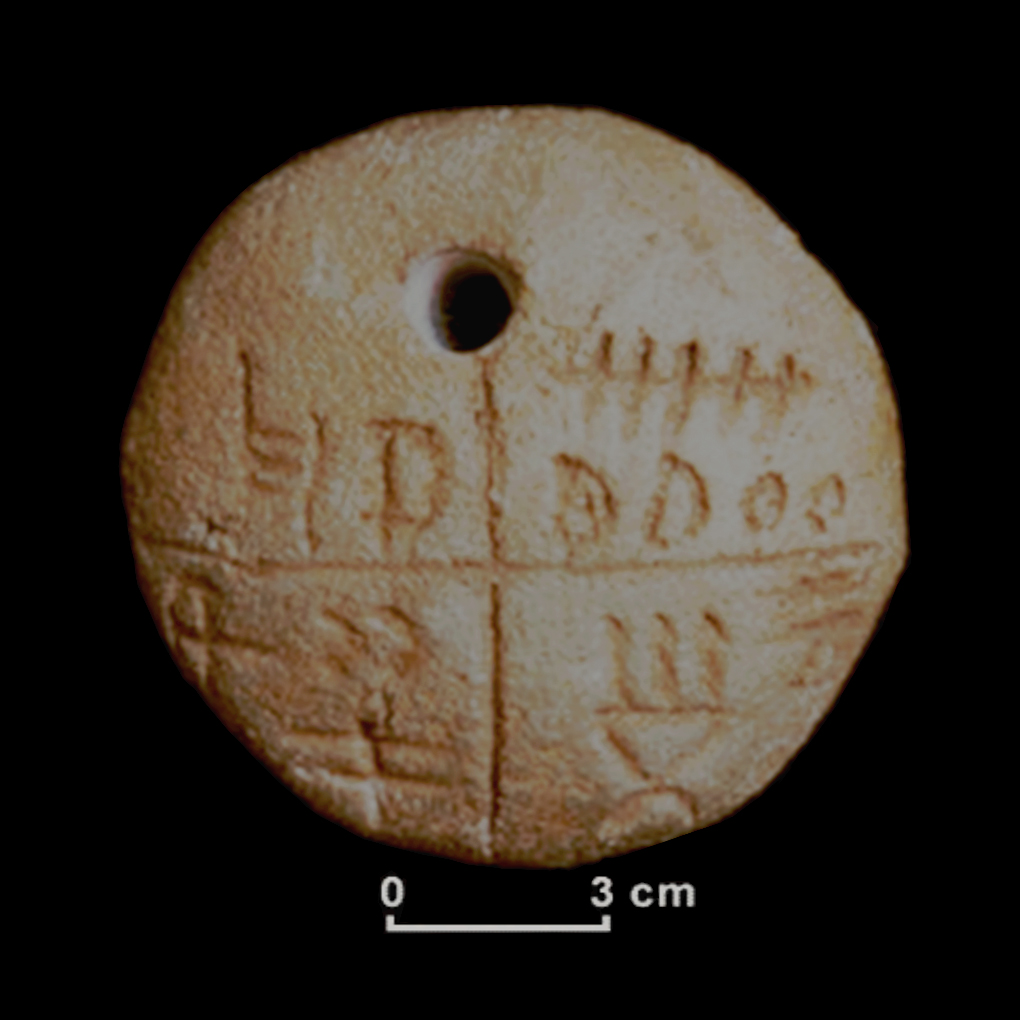 One of Tărtăria’s tablets | CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
One of Tărtăria’s tablets | CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
Age: From the Vinča-Turdaş culture during the Neolithic period, approximately 5300 BC. c.
The Tărtăria Tablets are a set of three clay tablets found in Romania and containing some of the earliest known examples of writing. These symbols raise questions about the development of written language and record-keeping in ancient European cultures.
21. Xaghra Stone Circle
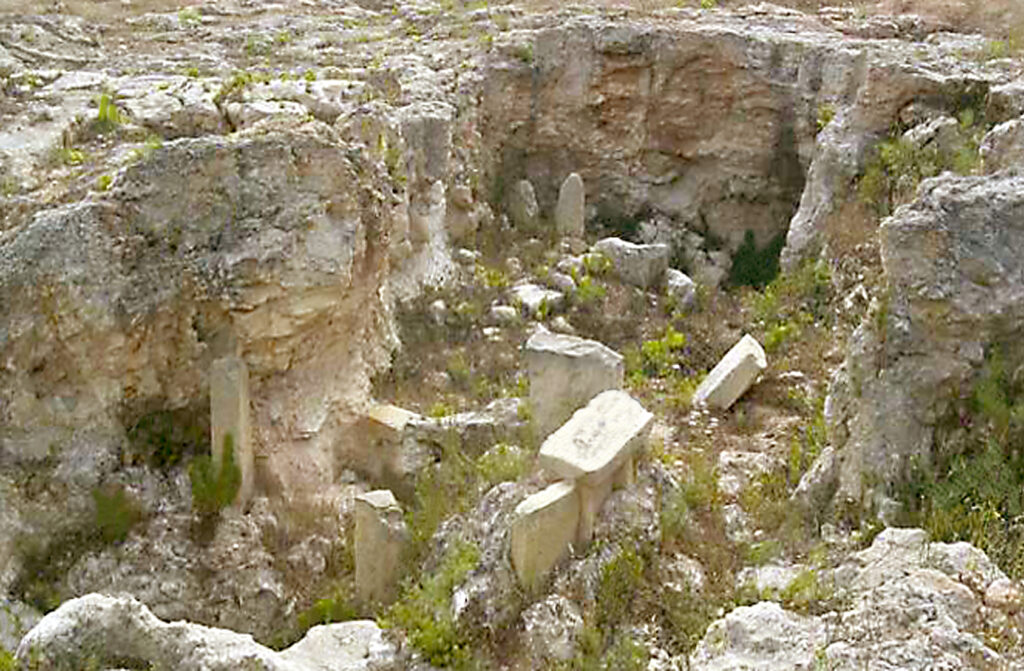 CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
Age: Neolithic, around 3,600 BC
The Xaghra Stone Circle is a megalithic structure located in Malta. It consists of vertical limestone megaliths arranged in a circular pattern. These stone circles are believed to have had ritual, astronomical or religious significance, and offered information about the spiritual practices of the island’s Neolithic societies.
22. The Thousands
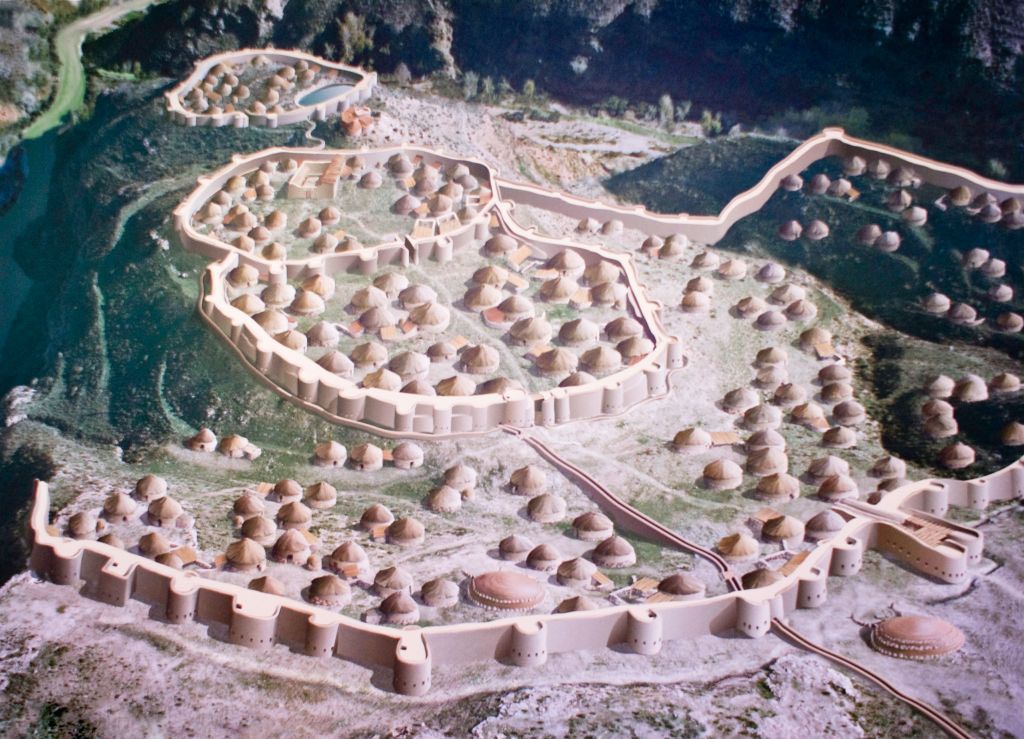 Model of the prehistoric town of Los Millares, with its walls. | CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
Model of the prehistoric town of Los Millares, with its walls. | CC BY-SA 4.0 WRITING
Age: Copper Age, around 3500 BC
Los Millares is a Neolithic and Copper Age fortified settlement located in Spain. This complex site includes stone walls, towers and a sophisticated water management system. It provides valuable information on the social organization and defense strategies of ancient European societies.
Conclusion
These extraordinary relics have transported us back in time and shed light on the ingenuity, creativity and adaptability of our ancient ancestors.
From the rudimentary but effective tools of Olduvai Gorge to the intricate and impressive rock art of Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc, these artifacts have offered glimpses into the daily life, spiritual beliefs, and technological achievements of Stone Age cultures. Worldwide. They represent the fundamental pillars of human civilization and are enduring testimonies to our enduring legacy.
As we reflect on these artifacts, we are reminded of the deep connections that bridge the chasm of time, linking us to those who created and used these tools, created stunning art, and left their indelible marks on history.
Faced with these ancient treasures, we remember the continuum of human history, where the echoes of the Stone Age still resonate, shaping our world today.
**Please note this post may contain affiliate links. When you book through one of our links we earn a small commission at no extra cost to you and goes a long way towards keeping the site up and running.


Related Post
A shocking documentary proves that mermaids do exist
SHOCKING Revelation: Thuya, Mother of Queen Tiye, Was the Grandmother of Akhenaten and Tutankhamun—What Ancient Egyptian Secrets Did She Leave Behind?
Breaking News: Astonishing Discoveries at Karahan Tepe Confirm an Extraterrestrial Civilization is Hiding on Earth, and NO ONE Knows!
Breaking News: Researchers FINALLY Discover U.S. Navy Flight 19 After 75 Years Lost in the Bermuda Triangle!
NASA’s Secret Investigation: Uncovering the Astonishing Mystery of the UFO Crash on the Mountain!
Explosive UFO Docs LEAKED: Startling Proof That Aliens Ruled Ancient Egypt!